Access to clean drinking water is not merely a luxury; it is a fundamental human right essential for nurturing health and promoting well-being. In the face of a burgeoning global population, the quest to ensure clean water for all communities is becoming increasingly difficult. The implications go beyond mere hydration; contaminated water can lead to various health issues, hampering the development, productivity, and even survival of populations. Continuous advancements in purification technology are imperative to address this dire public health concern.
Innovating Water Purification with Plant-Based Insights
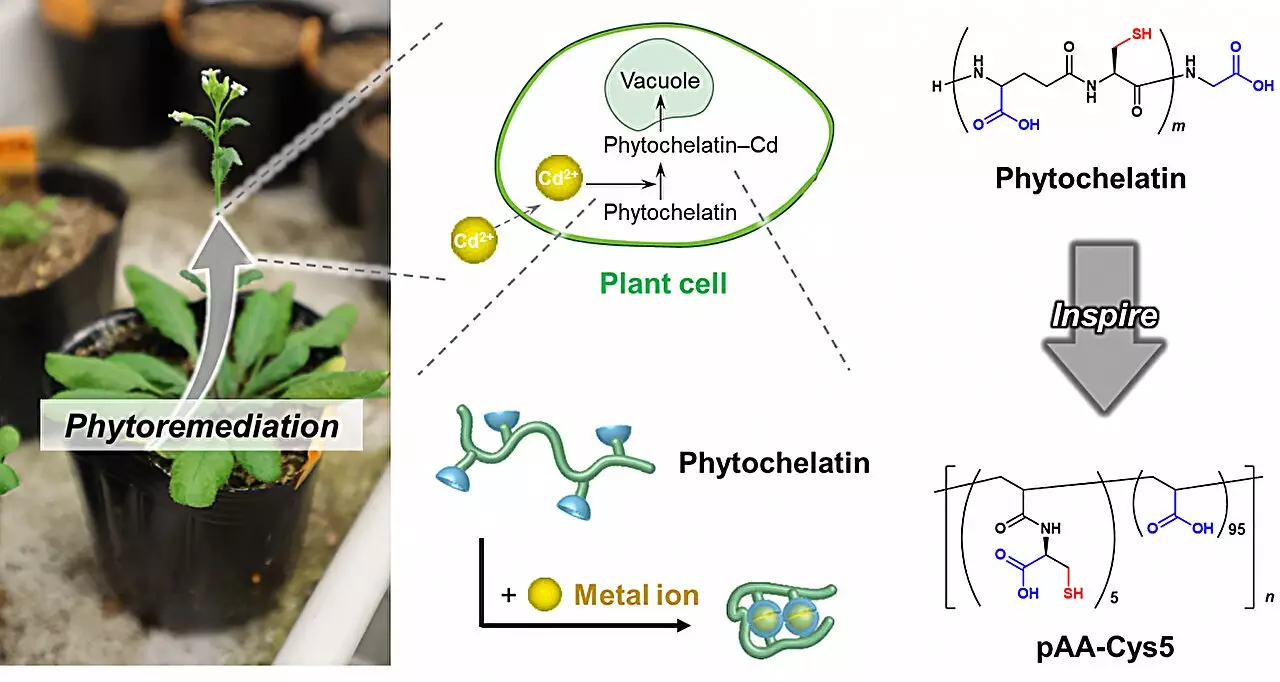
A recent study published in Nature Communications highlights promising advancements in water purification techniques inspired by nature. Researchers from the HeKKSaGOn Alliance, comprising leading scientists from prestigious institutions such as Kyoto University, Osaka University, and the University of Heidelberg, have developed a groundbreaking method to expunge harmful heavy metal ions from water. Their approach pivots on phytochelatin, a plant-derived protein that has been refined through evolution to specifically target and neutralize heavy metals.
Traditional water purification methods tend to be broad-brush approaches; they successfully eradicate contaminants but also eliminate necessary ions, which can render them inefficient for specific mineral needs. In contrast, phytochelatin’s selective binding ability stands out as a sophisticated alternative, demonstrating a targeted approach to purification.
Unlocking the Secrets of Phytochelatin
The researchers explored the molecular structure of phytochelatin, aiming to understand its selective properties. By concentrating on its building blocks—specifically, two chemical groups known as carboxylate and thiolate—they created a polymer that mimicked these natural components. This innovative polymer was subsequently integrated with silica beads and cellulose membranes, maintaining the essential properties that enable the binding and sequestering of toxic heavy-metal ions like cadmium.
The research team’s focus was to create a polymer that operated in a flow-through system, easily facilitating the movement of contaminated water and enhancing purification efficacy. Remarkably, their findings demonstrated that this approach could effectively reduce cadmium levels in water to safe drinking thresholds within just one hour.
The Polymer’s Competitive Edge
What sets this polymer apart is not just its ability to capture cadmium ions; its specificity reveals a remarkable potential for broader applications. The polymer also exhibits a strong affinity for mercury, further indicating its versatility in addressing various heavy metal pollutants. This specificity is crucial in the development of more efficient and targeted water treatment methodologies. The research provides evidence that not only are plants equipped with sophisticated mechanisms evolved for survival, but that we can harness and enhance those mechanisms through biotechnology for human benefit.
Implications for Sustainable Development
The findings hold monumental significance, particularly in regions where heavy metal contamination in water is prevalent. This polymer-driven technology could revolutionize water purification efforts, maximizing efficiency while minimizing the need for complex treatment processes. Moreover, the combination of plant-inspired innovation with modern polymer chemistry could pave the way toward sustainable and eco-friendly water treatment solutions.
As we confront the growing challenges of environmental degradation and water scarcity, the implications of these findings extend beyond simple technological advancements. They represent a step towards sustainable development and ecological conservation, strengthening the notion that natural systems can yield powerful tools for human innovation.
A Bright Horizon for Clean Water Access
The implications of this research are far-reaching, heralding a new era of water treatment technologies that marry ecological wisdom with advanced science. As our global community strives for equitable access to clean drinking water, innovations like the phytochelatin-inspired polymer shine as beacons of hope, epitomizing the synergy between the natural world and human ingenuity. By investing in such pioneering technologies, we not only aim to eradicate heavy metal contamination but also cultivate a future where safe drinking water is accessible to all, regardless of geographic or socioeconomic barriers.